Reasons For A Converter Failure
Your Catalytic Converter
Should Never Have Failed.
If It Did, Then You Have

Just replacing the converter Will
Not Fix The Problem
If your catalytic converter needs replacing,
one of the problems below most likely contibuted to its failure.
 Engine
Tune-Up Required.
Engine
Tune-Up Required.
A number of problems could occur to the catalytic converter as the result of an
engine that is out of tune. Any time an engine is operating outside proper
specifications, unnecessary wear and damage may be caused to the the catalytic
converter as well as the engine itself. The damage is often the result of an
incorrect air/fuel mixture, incorrect timing, or misfiring spark plugs. Any of
these conditions could lead to a catalytic converter failure or worse.
 Excess
Fuel Entering Exhaust.
Excess
Fuel Entering Exhaust.
The fuel that powers your vehicle is meant to burn in the combustion chamber
only. Any fuel that leaves the combustion chamber unburned will enter the
exhaust system and light-off when it reaches the catalytic converter. This can
super-heat the converter far above normal operating conditions and cause a Melt
Down.
Possible causes are an incorrect fuel mixture, incorrect timing, corroded spark
plugs, a faulty oxygen sensor, sticking float, faulty fuel injector or a
malfunctioning check valve.
 Oil
or Antifreeze Entering Exhaust.
Oil
or Antifreeze Entering Exhaust.
Oil or Antifreeze entering the exhaust system can block the air passages by
creating a heavy carbon soot that coats the ceramic catalyst. These heavy Carbon
Deposits create
two problems. First, the carbon deposits prevent the catalytic converter from
reducing harmful emission in the exhaust flow. And second, the carbon deposits
clog the pores in the ceramic catalyst and block exhaust flow, increasing
backpressure and causing heat and exhaust to back up into the engine
compartment. Your engine may actually draw burnt exhaust gasses back into the
combustion chamber and dilute the efficiency of the next burn cycle. The result
is a loss of power and overheated engine components. Possible causes are worn
piston rings, faulty valve seals, failed gaskets or warped engine components.
 Deteriorated
Spark Plug or Spark Plug Wires.
Deteriorated
Spark Plug or Spark Plug Wires.
Spark plugs that don't fire or misfire cause unburned fuel to enter the exhaust
system. The unburned fuel ignites inside the converter and could result in a
partial or complete melt down of the ceramic catalyst. Spark plugs and spark
plug wires should be checked regularly and replaced if damaged or if wires are
worn or cracked.
 Oxygen
Sensor Not Functioning Properly.
Oxygen
Sensor Not Functioning Properly.
An oxygen sensor failure can lead to incorrect readings of exhaust gasses. The
faulty sensor can cause a too rich or too lean condition. Too rich and the
catalyst can melt down. Too lean and the converter is unable to convert the
hydrocarbons into safe elements and may not pass a state inspection.
 Road
Damage or Broken Hangers.The ceramic catalyst inside a catalytic converter is made from a lightweight,
thin-walled, fragile material. It is protected by a dense, insulating mat. This
mat holds the catalyst in place and provides moderate protection against damage.
However, rock or road debris s triking the converter or improper or broken
exhaust system support can cause a Catalyst
Fracture.
Once the ceramic catalyst is fractured, the broken pieces become loose and
rattle around and break up into smaller pieces. Flow is interrupted and
backpressure in the exhaust system increases. This leads to heat build up and
loss of power. Possible causes of a catalyst fracture are road debris striking
the converter, loose or broken hangers, potholes or off-road driving.
Road
Damage or Broken Hangers.The ceramic catalyst inside a catalytic converter is made from a lightweight,
thin-walled, fragile material. It is protected by a dense, insulating mat. This
mat holds the catalyst in place and provides moderate protection against damage.
However, rock or road debris s triking the converter or improper or broken
exhaust system support can cause a Catalyst
Fracture.
Once the ceramic catalyst is fractured, the broken pieces become loose and
rattle around and break up into smaller pieces. Flow is interrupted and
backpressure in the exhaust system increases. This leads to heat build up and
loss of power. Possible causes of a catalyst fracture are road debris striking
the converter, loose or broken hangers, potholes or off-road driving.
After You Install
A New Catalytic Converter,

If your car caused the OEM catalytic converter to fail,
it could cause The New Converter
To Fail as well. And the warranty
that comes with a new replacement catalytic converter does not cover the type of
damage listed above.
WARNING:
A fine up to $2,500.00 can be assessed for removing or
tampering with a properly functioning catalytic converter.

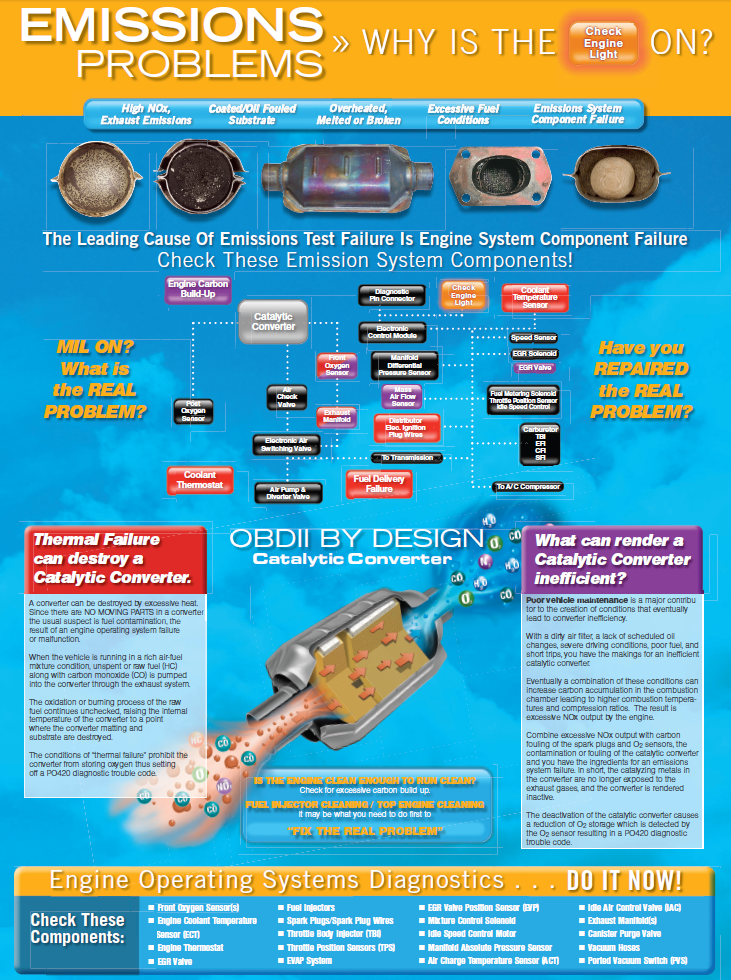
Identifying Emission Problems
Click here to return
to our home page

 Engine
Tune-Up Required.
Engine
Tune-Up Required. Excess
Fuel Entering Exhaust.
Excess
Fuel Entering Exhaust. Oil
or Antifreeze Entering Exhaust.
Oil
or Antifreeze Entering Exhaust. Deteriorated
Spark Plug
Deteriorated
Spark Plug Oxygen
Sensor
Oxygen
Sensor Road
Damage or Broken Hangers.
Road
Damage or Broken Hangers.

